All issues
Author:Yuan-Kai Tu, Han-Wei Chen, Min-Kun Chi, Shih-Lun Fang, Min-Hwi Yao, and Bo-Jein Kuo*
Abstract:
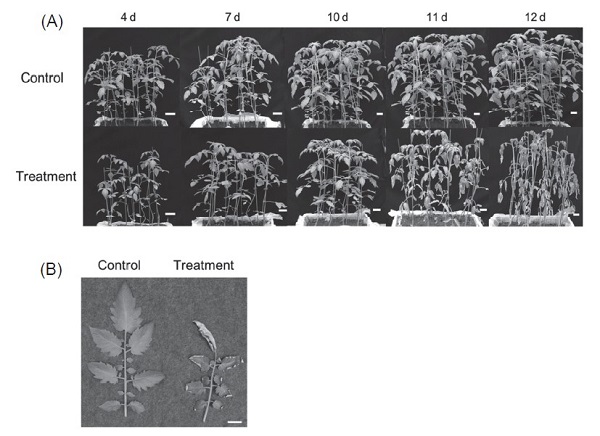
Hyperspectral data collection is a kind of non-destructive detection method, which can be applied to determine the physiological status and disease occurrence of plants. Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) is an important vegetable in Taiwan, and proper water management during growth process has crucial impacts on quality and yield. In order to establish a method for predicting the early stage of water deficit stress for tomatoes, ‘Rosada’ tomato seedlings were administrated with drought treatment and physiological parameters including the transpiration rate, stomatal conductance and assimilation rate were determined. During the period of experiments, the hyperspectral reflectance data of the leaf canopy were collected as well. The physiological status of tomato was further determined by the results of physiological parameters. Coupling with the hyperspectral data, the partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) was constructed to predict the early stage of stress status induced by drought treatment. The results showed that the transpiration rate, stomatal conductance, and assimilation rate were significantly lower than those of the control group 8, 9 and 10 d after drought treatment (P < 0.05), while the morphology appeared obvious phenotypic variation 11 d after drought treatment. We concluded that the early physiological response to water deficit stress occurred approximately 10−11 d after drought treatment. The prediction accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of the PLS-DA models obtained from 348−1,052 nm were at the range of 0.90−0.93, 0.87−0.89 and 0.92−0.95, respectively. The results indicated that the PLS-DA model possessed acceptable prediction performance. Furthermore, four important characteristic bands, 348−584, 638−817, 937−950 and 1,016−1,052 nm, which were selected from the regression coefficients and variable importance in the projection (VIP) scores. We established additional PLS-DA models by these characteristic bands, and the prediction accuracy, sensitivity and specificity were 0.86−0.93, 0.79−0.92 and 0.90−0.92, respectively. These results showed that PLS-DA models established by the characteristic bands had no significant improvement to the model performance. However, the models could reduce the cost of data collection and subsequent operations.
Key words:Hyperspectral data, Cherry tomato, Water deficit, PLS-DA
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors