All issues
Author:Han-Wei Chen, Mei-Chun Lin, Suh-Jen Lin, Ching-Shan Tseng, and Yuan-Kai Tu*
Abstract:
The 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing is a high-throughput and gold-standard approach employed in DNA barcoding technique for soil microbial community study. DADA2 implements the divisive amplicon denoising algorithm and produces higher-resolution data sets of amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) for the Illumina sequencing platform. The importance is even greater to link
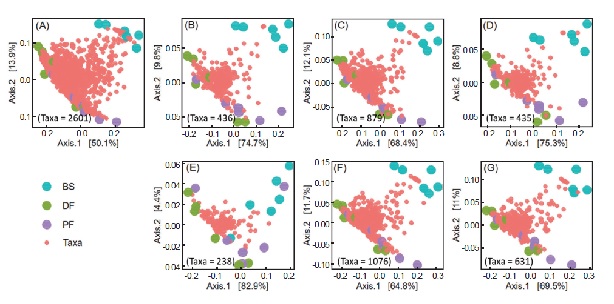
microbial binomial nomenclature and high-resolution ASVs data for subsequent community diversity analysis. In this study, we performed a comparative study of three taxonomic assignment pipelines using DADA2 processed datasets. The efficiency of taxonomic annotation showed that DADA2’s assign Taxonomy algorithm goes well with the SILVA 138 reference training set (with Species). Here we used a binary classification test to evaluate the ability of four DADA2-formatted reference training sets (SILVA 138, SILVA 138.1, GTDB, and RefSeq + RDP) in soil microbial classification. The results showed that the GTDB training set had the highest sensitivity, and both SILVA 138 and SILVA 138.1 training sets had the best specificity. While the RefSeq + RDP training set showed the best performing descriptors of accuracy, coverage, Matthews correlation coefficient, and positive predictive value than other training sets. However, the results of microbial diversity analysis showed that the taxonomic assignment of the GTDB training set was the closest to the original ASVs data, reflecting the best soil microbial community compositions. This study revealed that the selection of the taxonomic assignment pipelines and the 16S rDNA reference training set had a great impact on microbial identification. With the continuous updating of the 16S rDNA reference database, we should curate our taxonomic profiling results more carefully to obtain a better microbial diversity description.
Key words:Soil microbiota, Amplicon sequencing, DNA barcoding, DADA2
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors