All issues
Author:Po-An Lin*, Wan-Yi Liao, Shuay-Tsyr Ho, Chia-Wei Hsieh, and Tsung-Han Li
Abstract:
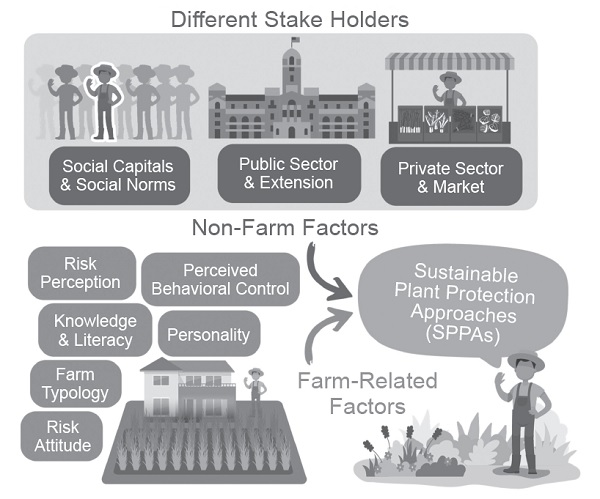
Adopting sustainable plant protection approaches (SPPAs) is critical for addressing environmental challenges and ensuring sustainable agricultural systems. This review synthesizes current knowledge on the factors influencing farmers’ adoption of SPPAs, focusing on behavioral, social, and institutional drivers. Farm-related determinants include health concerns, risk perceptions, economic stability, and literacy regarding SPPA benefits and implementation. Non-farm factors such as social norms, government policies, and stakeholder interactions also shape adoption behaviors. The role of social networks and extension services is underscored as critical mechanisms for knowledge transfer and motivation, with farmer-to-farmer interactions emerging as particularly influential. Despite evidence supporting the environmental and economic benefits of SPPAs, barriers such as high costs, perceived inefficacy, and limited access to information and technical resources persist. Government interventions, including subsidies, training programs, and crop insurance, are identified as key tools to mitigate risks and financial burdens associated with SPPAs. However, systemic issues, such as fragmented policies and conflicting market pressures, often hinder the adoption of SPPAs. This review highlights the need for integrated, evidence-based strategies that align incentives across stakeholders, leverage psychological insights into behavior change, and address regional and cultural differences in agricultural systems. Advancing SPPA adoption requires long-term research and coordinated efforts among researchers, policymakers, and the agricultural community to build resilient and sustainable farming practices globally.
Key words:Farmers’ behavior, Integrated pest management (IPM), Agricultural sustainability, Agricultural policy, Stakeholders
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Bacteria in Insect Pest Management in Agriculture: The Past, Present, and Future
- 2. Multiple Applications of Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor L.) Reared on Plant-Based Substrates: Circular Agriculture, Farmed Animal Feed, and Other High-Value Products
- 3. Mini-Review on Microbial Pesticide Research for Crop Protection Assisted by Generative AI
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors