All issues
Author:Chiao-Wen Huang*, Shu-Joan Zeng, Jin-Hsing Huang, and Jyh-Nong Tsai
Abstract:
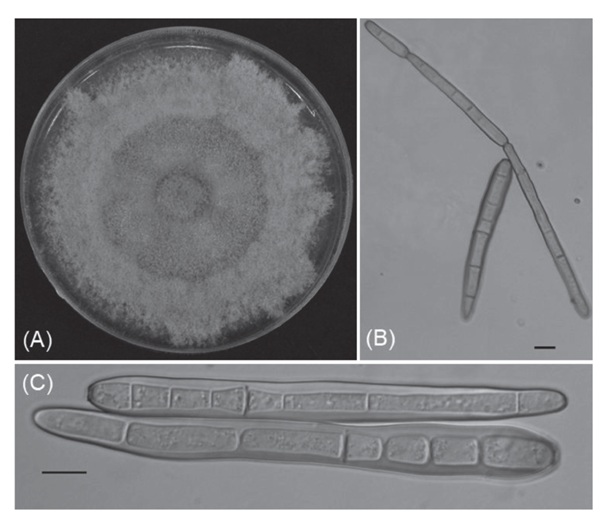
In July 2022, leaf spot disease of desert rose (Adenium obseum) occurred in the Changhua area, with symptoms showing brown, round, or irregular-shaped lesions on leaves. In severe cases, the affected leaves yellowed and dropped off prematurely. In this study, a fungus was isolated from the diseased leaves and cultured on potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium. The colony was grayish-white to gray, with the reverse side of the medium turning brown to black. The conidia of this fungus were cylindrical or barrel-shaped, straight or slightly curved, light brown, with multiple septa, and blunt at the apex. Based on the symptoms of the disease, the morphological characteristics of the pathogen, and molecular sequencing identification results, this fungus was identified as Corynespora cassiicola. Artificial inoculation tests confirmed that C. cassiicola was pathogenic to desert rose leaves, and Koch’s postulates were completed, proving this fungus to be the causal agent of desert rose leaf spot disease. The optimal temperature was 24−32℃ for mycelial growth of C. cassiicola and 20−28℃ for spore germination. Mycelial growth of the pathogen was effectively inhibited by Cyprodinil + Fludioxonil, Boscalid, and Oxine-copper. Spore germination of the pathogen was inhibited by Oxine-copper, Mancozeb, and Cyprodinil + Fludioxonil based on fungicide screening conducted in vitro. The findings of this study on the disease symptoms, pathogen morphology, growth temperature, and fungicide sensitivity can serve as a reference for future disease identification and control efforts. This is the first report of leaf spot disease on desert rose caused by C. cassiicola in Taiwan.
Key words:Desert rose (Adenium obseum), Leaf spot, Corynespora cassiicola, Fungicides screening
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Bacteria in Insect Pest Management in Agriculture: The Past, Present, and Future
- 2. Multiple Applications of Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor L.) Reared on Plant-Based Substrates: Circular Agriculture, Farmed Animal Feed, and Other High-Value Products
- 3. Mini-Review on Microbial Pesticide Research for Crop Protection Assisted by Generative AI
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors