All issues
Author:Hui-Zhen Lu, Tai-Chuan Wang, Shou-Horng Huang, and Chi-Nan Chen*
Abstract:
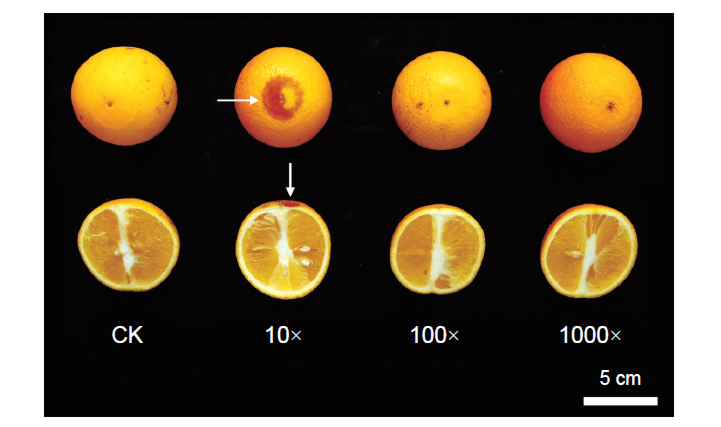
The oriental fruit fly [Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel)] is one of the most important pests in the world. The females lay eggs into fruit surface and hatch, then the larvae cause the damages of fruit dropping. Chemical control is widely used to manage the problem of oriental fruit flies by its low cost and fast control compared with other practices. This study focused on effects of some registered insecticides, which were used for pest management of sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) in Taiwan before. The fruits were dipped with 2.4% deltamethrin SC (1,500×), 50% malathion EC (800×), 30% spirodiclofen SC (5,000×), 2% abamectin EC (2,000×) in choice test. 4.5% azadirachtin EC in 10×, 100×, and 1,000× were used as positive control of deterrent oviposition, and water was used as negative control. The results showed that the females directly died by the treatments of deltamethrin, malathion and abamectin. The treatment of deltamethrin almost prevented the females from penetrating and laying eggs. The treatment of abamectin also suppressed laying eggs to fruit effectively. However, the treatment of malation did not have any oviposition deterrence effect. The treatment of azadirachtin could not kill the oriental fruit flies, but it reduced the numbers of laying eggs in oranges. In addition, the laying eggs decreased with the increasing of the concentrations of azadirachtin. Both 10× and 100× diluted azadirachtin revealed the greatest repellent effect in our experiment. The fruit quality and sensory evaluation for fruits were conducted after the application of insecticides. Drug spots appeared on the surface, and weight loss and odd smell were observed on the fruit treated with 10× azadirachtin. Overall, the deltamethrin was better than other insecticides for the control of oriental fruit flies in this study. Azadirachtin can inhibit the oviposition of oriental fruit fly, but inappropriate concentration of insecticides may affect fruit appearance and its quality. Therefore, the repellent treatment of azadirachtin integrated with other field techniques may have the potential to develop a new control method of oriental fruit fly in the future.
Key words:Bactrocera dorsalis, Citrus, Insecticide efficacy, Fruit quality analysis
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Using Digital Soil Mapping to Predict Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Zhuoshui River Basin
- 2. Taxonomic Review of the Genus Asiophrida Medvedev, 1999 in Taiwan (Insecta: Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Galerucinae: Alticini), with Notes on Biology
- 3. Development of a Technique for Forecasting (or Pre-Detection) Anthracnose Disease Incidences of Green Mature Bagging Mango Fruits
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors