All issues
Author:Yu-Ping Liang and Tai-Chuan Wang*
Abstract:
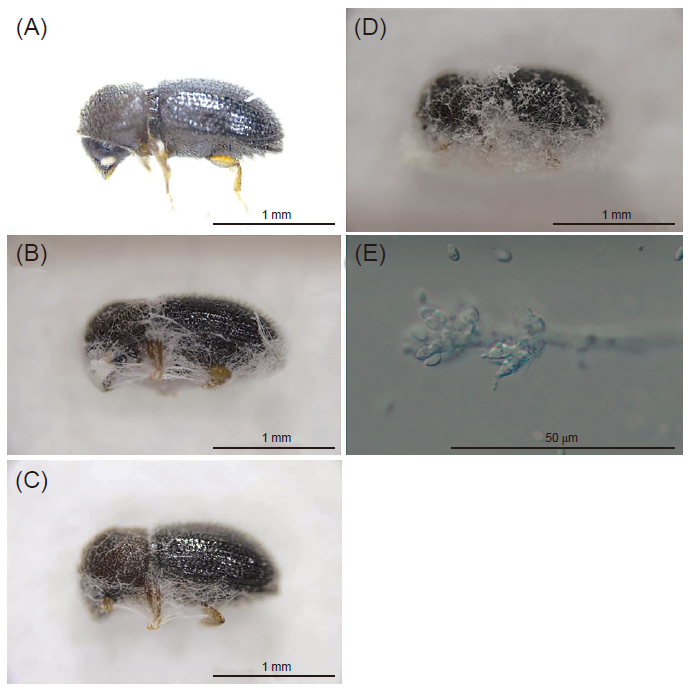
An isolate of entomopathogenic fungi, CAES1, was isolated from a naturally infected coffee berry borer (Hypothenemus hampei; CBB) in a coffee field in Taiwan. Colonies of CAES1 were white to pale-yellow or grey. Mycelia could grow in range of 10℃ to 30℃, with the optimal temperature at 25℃, ranging from 10℃ to 30℃. The conidiophores formed branches with phialides in whorls of 1 to 4, with phialides 3.7–5.0–6.4 μm × 1.9–3.0–3.5 μm, and conidia forming in chain, 2.7–3.8–5.4 μm × 1.2–1.6–2.1 μm. CAES1 was identified as Isaria javanica based on morphology and phylogenetic analysis of the sequences of ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS), translation elongation factor-1α (TEF1) and β-tubulin. The cumulative mortality rate of CBB was 100% on the 7th day after treated with conidia of I. javanica CAES1. I. javanica CAES1 sporulated on the surface of CBB 2.77 d ± 0.17 d after CBB died. This is the first record of I. javanica from CBB in Taiwan. It is suggested that I. javanica CAES1 is pathogenetic to the CBB and could be a potential biocontrol agent against CBB in the future.
Key words:Coffee berry borer (Hypothenemus hampei), Isaria javanica, Taiwan, Biological control
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Using Digital Soil Mapping to Predict Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Zhuoshui River Basin
- 2. Taxonomic Review of the Genus Asiophrida Medvedev, 1999 in Taiwan (Insecta: Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Galerucinae: Alticini), with Notes on Biology
- 3. Development of a Technique for Forecasting (or Pre-Detection) Anthracnose Disease Incidences of Green Mature Bagging Mango Fruits
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors