All issues
Author:Lit-Fu Chan*, Hsiu-Ying Lu, and Ru-Ping Lee
Abstract:
This study evaluated the performance of 16 electronic literature databases used by 16 research units of Council of Agriculture (COA), Executive Yuan in 2021–2022. Using data such as full-text downloads, citations and ordering costs, combined with download and citation analysis, we found out researchers’ behaviors and patterns using various types of literature and evaluated whether the
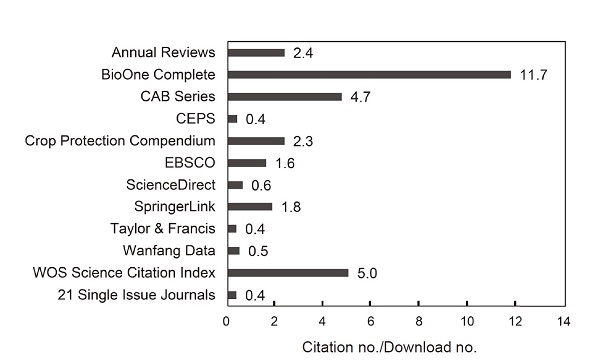
purchased literature resources meet research needs and rational use of funds. The results showed that the average cost per download and per citation varied greatly among electronic literature databases. Researchers preferred to search and download Chinese journals first. Due to the low price of Chinese literature databases, it showed that their use was more cost-effective. English journals were the most important literature resources cited by researchers when researchers developed agricultural research. The English citations of research reports published in Science Citation Index (SCI) and non-SCI journals were as high as 91.4% and 74.1% respectively. Since the price of professional literature databases in foreign languages is usually expensive, it was difficult to demonstrate the use performance in terms of the cost-effectiveness of downloads and citations. For citations in published reports, periodical literature was the primary source of information, accounting for 77.5%. According to the analysis of citation timeliness, the literature in the past 20 years guaranteed nearly 80% of the citations, which was the key part of the literature information. There was no correlation between the counts of full-text downloads and citations used by researchers using the database. The more types of journals covering important agricultural topics, the more specialized the subject is, and the more English-language journals are based, the more likely the downloaded journal literature will be referenced. Libraries should comprehensively consider various factors to build their collections, and avoid taking the usage rate as the only criterion for deletion. The data comparison process and multiple performance indexes established by this research can be used as an important evaluation basis for purchasing electronic literature resources of library collections in the future.
Key words:Electronic literature database, Citation analysis, Full-text downloads, Performance index, Cost-effectiveness.
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Using Digital Soil Mapping to Predict Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Zhuoshui River Basin
- 2. Taxonomic Review of the Genus Asiophrida Medvedev, 1999 in Taiwan (Insecta: Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Galerucinae: Alticini), with Notes on Biology
- 3. Development of a Technique for Forecasting (or Pre-Detection) Anthracnose Disease Incidences of Green Mature Bagging Mango Fruits
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors