All issues
Author:Yu-Ping Liang and Hui-Fang Ni*
Abstract:
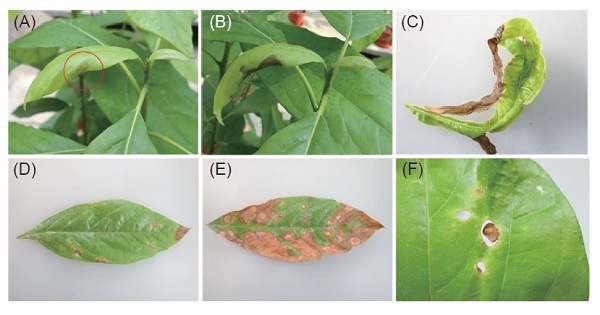
Phytophthora root rot (PRR) caused by Phytophthora cinnamomi is one of the most important avocado diseases in Taiwan. Though foliar sprays of phosphonate fungicides have been used to manage this disease in other countries, the most effective application dosage and techniques have not been determined for avocado cultivars planted in Taiwan. To provide information for optimizing phosphite application strategies, this study investigated the effects of different phosphite spray formulas on avocado seedlings of various cultivars, focusing on phytotoxicity and phosphite uptake. The results showed that 0.1% and 0.2% phosphite caused mild (phytotoxicity score < 2) or no phytotoxic damage on seedlings of 6 avocado cultivars tested, including ‘Choquette’, ‘Changan’, ‘Hung Shin Yuan’, ‘Zongpu Green Skin’, ‘Hall’, and ‘CAES3’, while 0.5% phosphite could cause severe phytotoxic damage (phytotoxicity score ≥ 2) on ‘Choquette’, ‘Changan’, and ‘Hall’ under high temperature. In addition, pH had no obvious effect on phytotoxicity when the solutions were buffered to a pH ranging from 6.5 to 7.5. A detached root bioassay showed that, compared with the control, the colonization rates of P. cinnamomi were significantly lower in ‘Changan’ seedlings treated with phosphite and an adjuvant (0.2% phosphite plus Jia-Shou-Huo-Jhan (加收活展, JSHJ), 0.5% phosphite plus JSHJ, or 0.5% phosphite plus S-408), and the root phosphite concentrations were above 180 μg g-1 for all these three treatments. Moreover, adding an adjuvant (JSHJ or S-408) to the phosphite solution reduced phytotoxic damage and increased the uptake of phosphite into the roots. The results generated from in this study will be helpful for the optimization of phosphite application strategies for the avocado industry.
Key words:Avocado, Adjuvant, Phosphite, Phytophthora root rot, Phytotoxicity
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Using Digital Soil Mapping to Predict Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Zhuoshui River Basin
- 2. Taxonomic Review of the Genus Asiophrida Medvedev, 1999 in Taiwan (Insecta: Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Galerucinae: Alticini), with Notes on Biology
- 3. Development of a Technique for Forecasting (or Pre-Detection) Anthracnose Disease Incidences of Green Mature Bagging Mango Fruits
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors