All issues
Author:Ssu-Yu Lin, Jau-Yueh Wang, Cheng-Bin Li, Han-Wei Chen, Da-Gin Lin, and Yuan-Kai Tu*
Abstract:
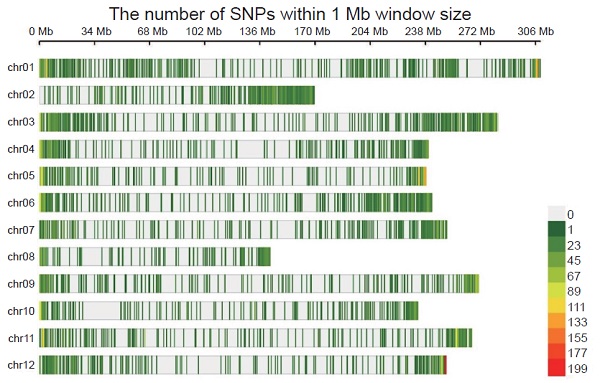
Next-generation sequencing technologies lead to a new era of crop genetic research. To lower sequencing costs for building a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) map of a genome, the reduced representation genome sequencing technology was used to sequence the flanking DNA sequences of selected restriction enzyme sites of DNA samples. However, appropriate parameters for constructing the reduced representation sequencing library, such as the choice of restriction enzyme and sequencing depth, differ in target crops and population composition. As a result, methodological adjustments toward target crops and population composition are vital to maximizing the efficiency of sequencing resources. In this study, we presented a tailored double-digest restriction site-associated DNA sequencing (ddRAD-seq) genotyping method for pepper germplasm. In the first part of this work, the performance of two restriction enzyme pairs- PstI/MspI and PstI/MseI were assessed, and results of in silico simulation showed 2.01% and 0.34% fragments of the total digested fragment were sequenced, respectively. According to sequencing results, more uniquely mapped and adequately paired reads (19–28 M) were observed in PstI/MspI pair than in PstI/MseI (15–17 M). Therefore, in terms of resource utilization in library preparation, the enzyme pair PstI/MspI performed better than PstI/MseI. In addition, the number or ratio of reads that came from PstI/MspI digestion was more efficiently mapped to the reference genome. As for the second part of this work, the SNP maps of 28 pepper accessions belonging to 5 domestic species were constructed using the ddRAD-seq genotyping technique with PstI/MspI restriction enzyme combination. A total of 14,230 high-quality SNP were obtained and distributed evenly on the 12 chromosomes of pepper. Furthermore, as expected, the 28 pepper accessions were clustered into proper phylogenetic groups based on the principle component analysis and the dendrogram analysis. In summary, the ddRAD-seq genotyping technique was tailored to construct the SNP maps of the pepper germplasm in this study.
Key words:Reduced genome sequencing, Double-digest restriction enzyme, Capsicum, Genome analysis
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Using Digital Soil Mapping to Predict Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Zhuoshui River Basin
- 2. Development of a Technique for Forecasting (or Pre-Detection) Anthracnose Disease Incidences of Green Mature Bagging Mango Fruits
- 3. Taxonomic Review of the Genus Asiophrida Medvedev, 1999 in Taiwan (Insecta: Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Galerucinae: Alticini), with Notes on Biology
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors