All issues
Author:Shiang-Shiuan Yu and Yun-Sheng Lu*
Abstract:
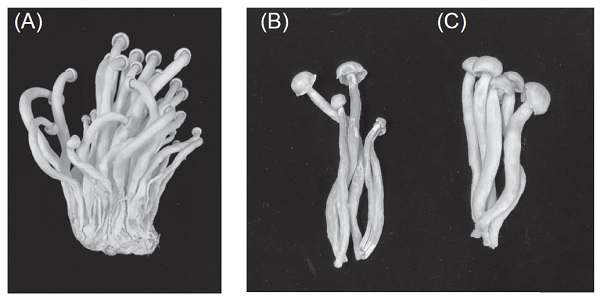
Hypsizygus marmoreus (Peck) H. E. Bigelow 1976, commonly known as the white elf mushroom (白精靈菇) when cultivated in a sawdust bag, is a commercially important mushroom species in Taiwan. In March 2023, infected samples showing yellow sticky symptoms on the lower parts of stipes were collected from a cultivated farm in Changhua, Taiwan. Bacterial ooze was observed flowing out of the infected stipes when they were suspended in sterile water. The isolated bacterium from the infected fruiting bodies was grown on a nutrient agar (NA) medium, forming circular colonies with smooth surfaces and a milky yellow color. It also exhibited yellow-green fluorescence on King's B medium. To confirm the pathogenicity of the bacterial isolate on white elf mushroom, its suspension in sterile water was sprayed on the surfaces of fruiting bodies, resulting in yellow and water-soaked symptoms within 1–3 d after inoculation. Over time, the symptoms expanded, leading to severe brown blotching and rot of the fruiting body tissues, accompanied by a sticky odor on the 7 d after inoculation. Based on the results of observation of cultural characteristics and pathogenicity tests that conform to Koch’s postulates, as well as the result of 16S rRNA sequence analysis, the causal agent of the bacterial brown blotch disease on white H. marmoreus was identified as Pseudomonas tolaasii Paine. This paper represents the first report of bacterial brown blotch disease on white H. marmoreus in Taiwan. In the future, further surveys of the brown blotch disease in different cultivation areas are needed. Additionally, the disease control effect of environmental disinfectants such as hypochlorous acid-containing water will be tested to reduce the economic losses caused by the bacterial disease.
Key words:White Hypsizygus marmoreus, Bacterial Brown Blotch, Pseudomonas tolaasii
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Using Digital Soil Mapping to Predict Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Zhuoshui River Basin
- 2. Taxonomic Review of the Genus Asiophrida Medvedev, 1999 in Taiwan (Insecta: Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Galerucinae: Alticini), with Notes on Biology
- 3. Development of a Technique for Forecasting (or Pre-Detection) Anthracnose Disease Incidences of Green Mature Bagging Mango Fruits
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors