All issues
Author:Wen-Bin Feng, Chi-Yang Lee, Tai-Chuan Wang, and Me-Chi Yao*
Abstract:
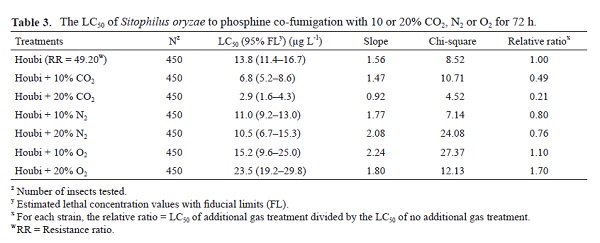
Sitophilus spp. is the most serious pest in imported brown rice warehouses, and its phosphine resistance has been observed in Taiwan. To overcome the efficiency decline of phosphine fumigation to Sitophilus beetles, phosphine fumigation with additional gas is the most noticed practice internationally. In this study, we evaluated the toxicity increase of phosphine in the presence of additional 10–20% of CO2, O2, or N2 to Sitophilus beetles for 20 h or 72 h of fumigation. We found that there was no synergism between phosphine and additional gas for phosphine-resistant Sitophilus oryzae (Linnaeus) strains with 20 h fumigation. However, when the fumigation period prolonged to 72 h, the LC50 of phosphine with additional 10 or 20% of CO2, or N2 decreased from 13.8 to 2.9–11.0 μg L-1 for Houbi strain of S. oryzae. We consider that additional CO2, and N2 can potentially enhance the toxicity of phosphine against phosphine-resistant stored-product pests in the imported rice warehouse.
Key words:Sitophilus, Phosphine, CO2, O2, N2
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Using Digital Soil Mapping to Predict Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Zhuoshui River Basin
- 2. Development of a Technique for Forecasting (or Pre-Detection) Anthracnose Disease Incidences of Green Mature Bagging Mango Fruits
- 3. Taxonomic Review of the Genus Asiophrida Medvedev, 1999 in Taiwan (Insecta: Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Galerucinae: Alticini), with Notes on Biology
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors