All issues
Author:Pao-Jen Ann*, Ien-Tien Wang, and Jyh-Nong Tsai
Abstract:
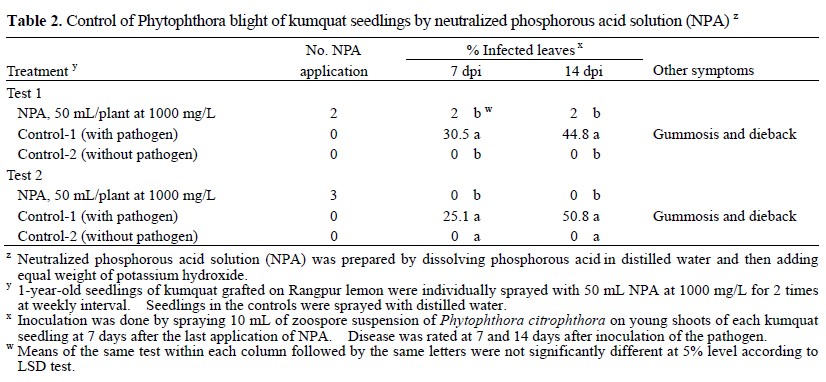
A greenhouse study was conducted to determine effects of neutralized phosphorous acid solution (NPA) on control of Phytophthora diseases of kumquat (Fortunella margarita) grafted on Rangpur lemon (Citrus limon), loquat (Eriobotrya japonica cv. ‘Mogi’) and avocado (Persea americana cv. ‘Tainan’). The NPA solution was prepared by dissolving phosphorous acid in water and then adding equal weight of potassium hydroxide to the solution. For kumquat, 1-year-old seedlings were sprayed with NPA solution (1000 mg/L), 50 mL/seedling, for 2 or 3 times at weekly interval and then sprayed with zoospore suspensions of Phytophthora citrophthora, 10 mL/seedling, at 7 days after last NPA spray. After inoculation for 14 days, each seedling was recorded for disease incidence on leaves. In another experiment, 5-year-old kumquat plants grafted on Rangpur lemon were sprayed with NPA (1000 mg/L), 500 mL/plant, for 3 times at weekly interval and inoculated with the pathogen, 200 mL/plant, at 7 days after last NPA spray. For loquat, 6-month-old seedlings were treated with NPA (2000 mg/L) by soil drenching or with NPA (1000 mg/L) by spraying for 3 times at 30-day interval. The seedlings were then inoculated with Phytophthora nicotianae by placing one gram of pathogen-colonized wheat-oat grains on the wounded area of basal stems. For avocadoes, 6-month-old seedlings were inoculated with Phytophthora cinnamomi by drenching with 100 mL of chlamydospore suspension on each plant and then treated with NPA (1000 or 2000 mg/L) by soil drenching for 3 times at 3-month interval. Results showed that spraying kumquat seedlings with NPA at 1000 mg/L (a.i.) for 2–3 times significantly reduced seedling blight (< 2% infected leaves) caused by P. citrophthora, compared to untreated controls (> 44.8% infected leaves). Similarly, NPA sprayed three times on 5-year-old kumquat plants was also effective in reducing incidence of Phytophthora fruit rot, leaf blight and twig blight. Application of NPA at 2000 mg/L by soil drenching or at 1000 mg/L by spraying completely controlled basal stem rot of loquat caused by P. nicotianae, whereas more than 60% of seedlings were killed in the controls. The avocado seedlings treated with NPA by soil drenching and inoculated with the pathogen were all survived during the test period, whereas 50–60% seedlings were killed in the pathogen-inoculated control. Avocado seedlings treated with NPA were taller and heavier than the pathogen-inoculated control, but they were shorter and lighter than the non-inoculated control. This study reveals that NPA is a chemical with potential for practical use in the management of Phytophthora diseases of kumquat, loquat and avocado.
Key words:Phosphorous acid, Phytophthora diseases, P. cinnamomi, P. citrophthora, P. nicotianae, Disease control, Kumquat, Avocado, Loquat
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors