All issues
Author:Yih-Juh Shiau* and Wan-Lun Ho
Abstract:
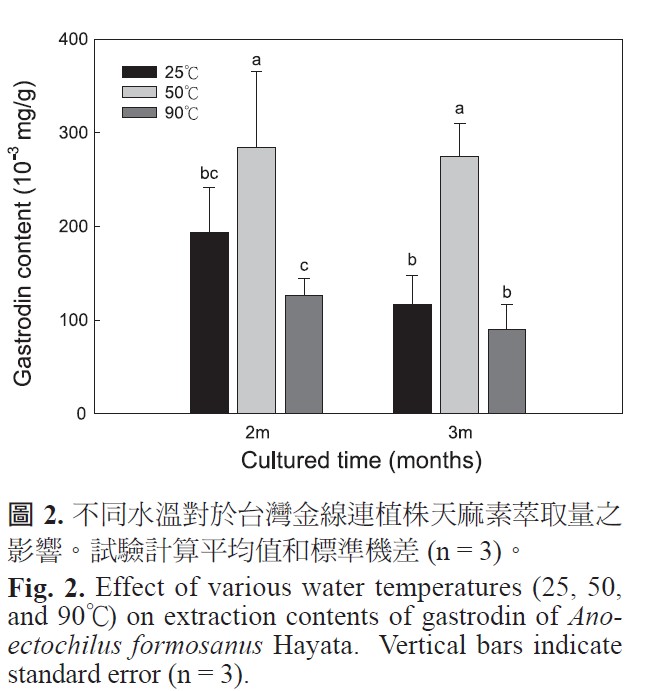
Gastrodin is a phenolic compound. It is one of the important secondary metabolites in Anoectochilus formosanus Hayata. The objectives of this study were to establish the method for extraction of gastrodin from A. formosanus and to compare contents of gastrodin in various parts of plants of A. formosanus. Results showed that the proper procedure for extraction of gastrodin from fresh tissues of A. formosanus was by extraction of gastrodin from freeze-dried tissues at 50℃, using deionizer water as solvent. The content of gastrodin extracted with deionizer water was 300.8 μg·g-1 ± 43.6 μg·g-1, and it was signifcantly higher than those samples extracted by the solvents of 99.9% methanol, 95% ethanol, and 50% ethanol. The content of gastrodin in A. formosanus roots was 2241.7 μg·g-1, which was signifcantly higher than gastrodin in the samples of fowers (660.0 μg·g-1 ± 179.1 μg·g-1), leaves (402.5 μg·g-1 ± 50.8 μg·g-1), rachis (285.0 μg·g-1 ± 35.4 μg·g-1) or stems (273.3 μg·g-1 ± 33.3 μg·g-1). This study indicates that roots of A. formosanus are the best tissues for extraction of gastrodin and that the testing procedure described in this study is useful for selection of A. formosanus plantlets with high contents of gastrodin.
Key words:Anoectochilus formosanus Hayata, Extraction, Gastrodin
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors