All issues
Author:Tseng-Wei Tan* and Kuei-Nuan Chen
Abstract:
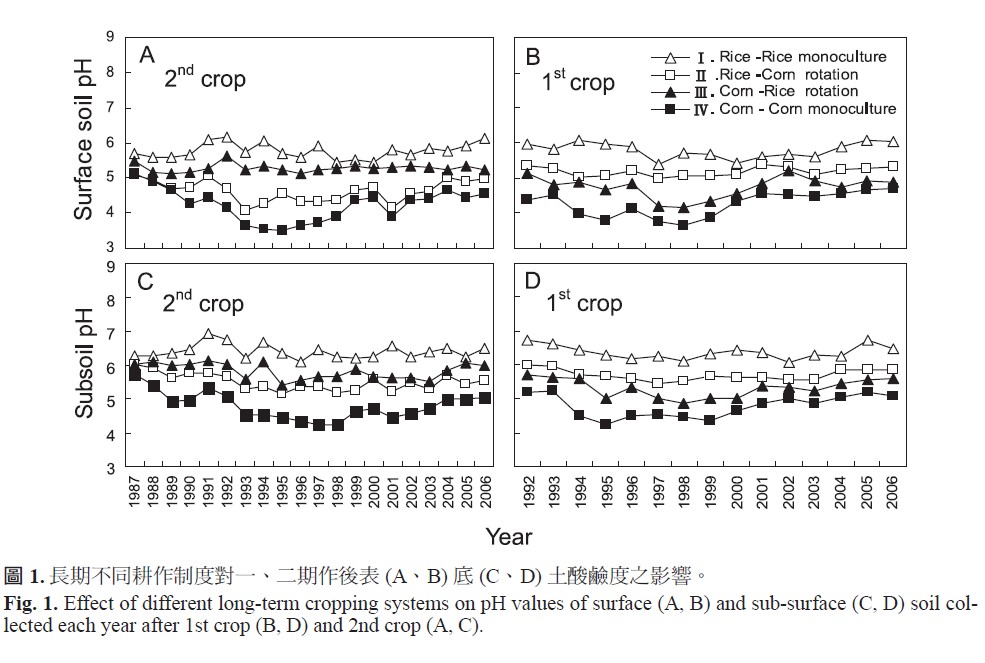
The objective of this study was to determine effect of long term application of chemical fertilizers on soil pH in different cropping systems. The long-term feld experiment was conducted from 1987 to 2006 in a feld of noncalcareous sandstone and slate alluvial soil at the farm of TARI. There were four treatments in this study, including rice monoculture, corn monoculture, rice-corn rotation and corn-rice rotation. The fertilizers for each rice crop were 124 kg N/ha, 140 kg P2O5/ha, and 70 kg K2O/ha, whereas the fertilizers for each corn crop were 270 kg N/ha, 140 kg P2O5/ha, and 70 kg K2O/ha. Results of the 20-year test showed that cropping systems have signifcant effects on pH values of soil and the maximum effect was the treatment of corn in monocropping, followed by the treatment of rice in monocropping, and the minimum effect in the treatments of rice-corn rotation and corn-rice rotation. The pH value of topsoil or subsoil was the highest in the treatment of rice monocropping, followed by the treatments of crop rotation, and the lowest in the treatment of corn monocropping. According to the relations between the pH value and the years, the pH value under rice monocropping and rice-corn rotation did not have progressively increasing or decreasing of soil pH year by year. However, the pH value of soil showed the drastic decreasing with years in the treatment of corn in monocropping. These results indicate that continuous monocropping of corn under dryland conditions and the application of high amount of ammonium-based N fertilizers for this crop are the major contributors to soil acidifcation. Therefore, pedogenic processes of paddy soils are important in maintaining the stability of soil pH and soil fertility in intensive agriculture.
Key words:Cropping system, Monoculture, Rotation, Soil pH
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors