All issues
Author:Hui-Fang Ni, Shu-Li Hsu, Ruey-Shyang Chen, and Hong-Ren Yang*
Abstract:
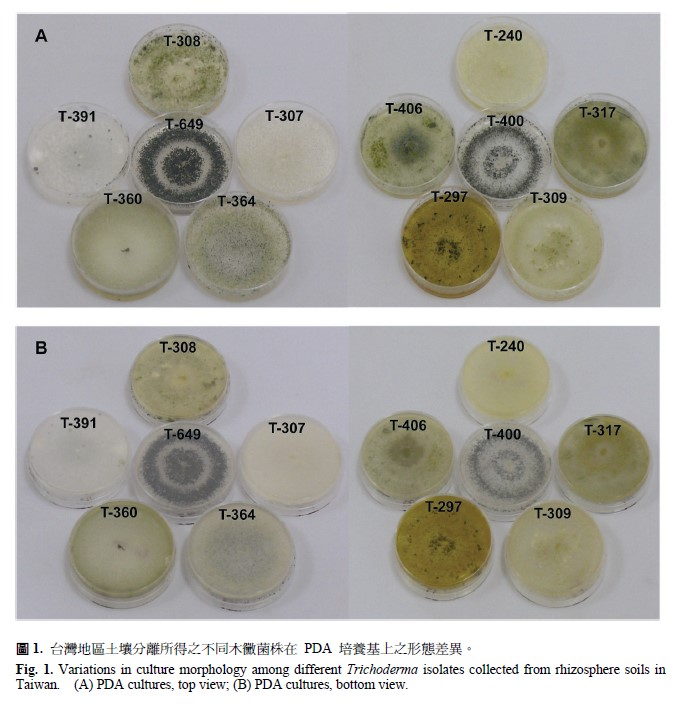
A total of 643 isolates of Trichoderma spp. were obtained from rhizosphere soils in central and southern Taiwan. Among them, 301 isolates were assayed in vitro for antagonism on the fungal plant pathogens, Botrytis elliptica, Phellinus noxius, Sclerotium rolfsii, and Phytophthora capcisi, using for cellophane paper method. Results showed that two of the isolates, Tri-003 and Tri-080, completely suppressed the mycelial growth of these four fungal pathogens. Tri-003 and Tri-080 were further tested for antagonism on seven species of other fungal plant pathogens and the results showed that these two isolates also completely inhibited mycelial growth of Peronophythora litchi and Pythium sp. Results of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) of rDNA sequence of Tri-003 and Tri-080 isolates showed a sequence identity of 99% with Trichoderma virens. Based on morphological and molecular studies, the identity of both Tri-003 and Tri-080 belongs to T. virens. The potential of these two antagonistic isolates of Trichoderma for control of plant diseases caused by Phytophthora spp., Pythium spp., and Phellinus noxius warrants further investigations.
Key words:Trichoderma virens, Antagonism, Fungal plant pathogens, Biocontrol
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors