All issues
Author:Ming-Hwi Yao*, Chun-Jen Chen, and Guo-Sheng Huang
Abstract:
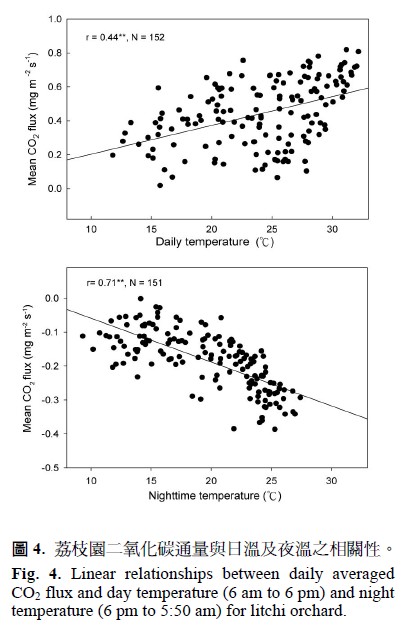
This research was conducted in the orchards of litchi (Litchi chinensis) to solve the problem of monitoring physiological responses of fruit trees in large field areas using the technique of flux measurement. Carbon dioxide flux was used to evaluate the carbon fixation capacity in litchi canopy. The value of latent heat flux can represent the actual evapotranspiration of the litchi orchard. Results of long term monitoring data collected in the orchard showed that the carbon dioxide flux was highly correlated to the solar radiation (r = 0.87) and the night temperature (r = 0.71). The latent heat flux was highly correlated to the vapor pressure deficit which was calculated by measuring temperature and relative humidity (r = 0.70). However, there were no good relationships between the latent heat flux and the commonly used water monitoring indices such as soil water content, sap flow in stem, leaf transpiration and values of differences between canopy temperature and air temperatures. Therefore, this study suggests that the vapor pressure deficit is a good index for the water management in litchi orchards.
Key words:Litchi, Litchi chinensis, Latent heat, CO2 flux, Energy balance, Evapotranspiration
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors