All issues
Author:Jiunn-Feng Su, Yi-Ching Lee, Lan-Yi Chien, and Ting-Fang Hsieh*
Abstract:
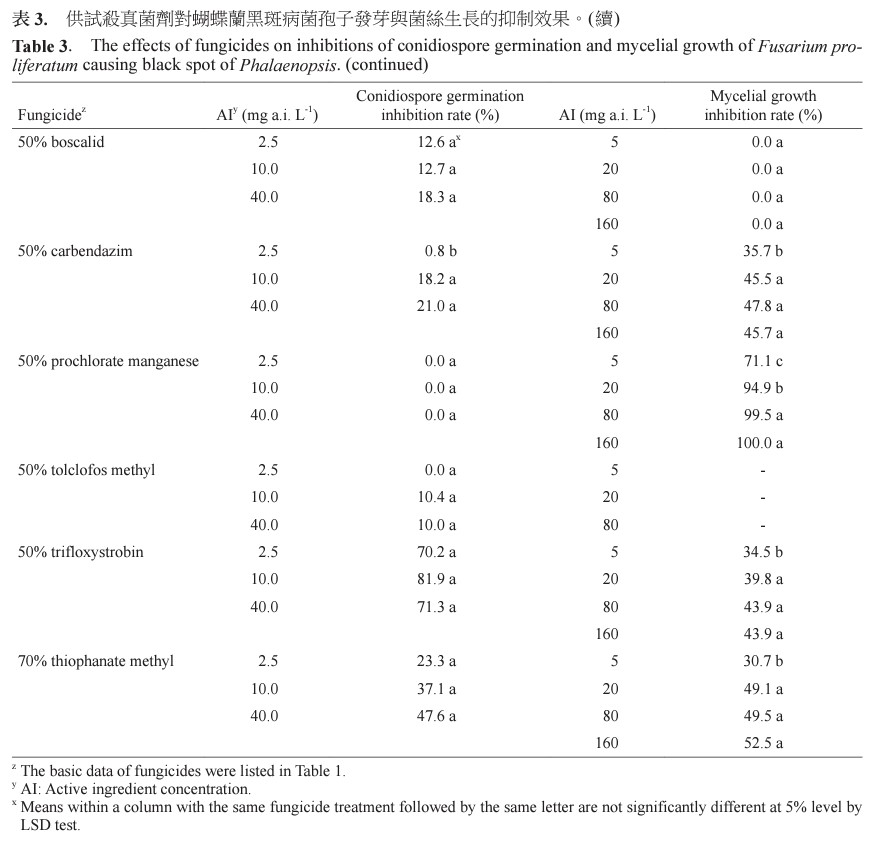
Fusarium diseases of Phalaenopsis, including yellow leaf caused by Fusarium solani, gray spot caused by Fusarium oxysporum and black spot caused by Fusarium proliferatum, were frequently found in the fields. Sixteen fungicides were selected for evaluating the inhibition effect of conidiospore germination and mycelium growth of these three pathogens. On inhibition of conidiospore germinations, data showed that inhibition rates of F. solani and F. proliferatum by 10 mg a.i. L-1 dilution concentration of 40% iminoctadine triacetate and 23.6% pyraclostrobin were more than 99%. And inhibition rates of F. oxysporum by 2.5 mg a.i. L-1 dilution concentration of 50% trifloxystrobin and 23.6% pyraclostrobin were more than 82%. On the inhibition of mycelial growth, data showed that the inhibition rates by 5 mg a.i. L-1 dilution concentration of 25% prochloraz and 50% prochlorate manganese were more than 60%, better than other tested fungicidies.
Key words:Phalaenopsis diseases, Fusarium pathogen, Fungicide
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors