All issues
Author:Chiao-Yi Huang, Szu-Yi Chou, Ya-Lin Lee, Wen-Bin Tseng, Chun-Wei Chen, Chang-Sheng Wang*, and Da-Gin Lin*
Abstract:
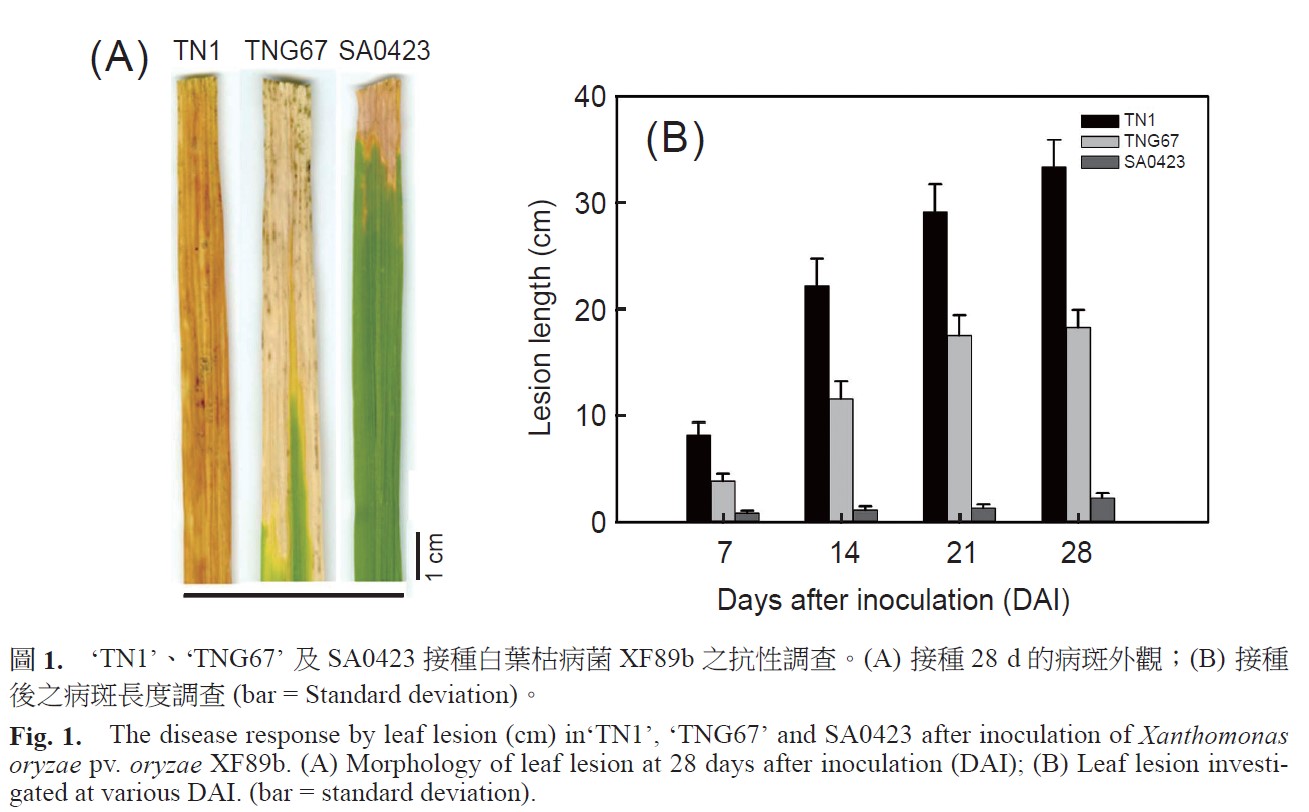
Bacterial blight disease, caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, is one of the most serious diseases in rice. To explore novel resistant genes in SA0423, harbored with broadly resistance against rice bacterial blight disease (RBBD), the transcriptomes of ‘TNG67’ and SA0423 were determined by microarray technologies with the RNA samples prepared from the leaves collected at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, and 6 h, respectively, after inoculation of XF89b, atypical isolate used in Taiwan nursery. One-way analysis of variance and Student-Newman-Keuls (SNK) test displayed that 2,727, 3,585, and 18,432 differentially displayed transcripts were found only in SA0423, ‘TNG67’, and both lines, respectively. Fifty-nine genes that might involve in providing the resistance in SA0423 were determined by bioinformatics analysis such as annotation of metabolic pathway, comparative mapping analysis with published resistance loci, “plant-pathogen interaction” pathway, and clustering with BioLayout Express3D. By confirming with real-time RT-PCR, 17 resistance gene candidates were selected in this work. Through bioinformatic analysis, results showed that they might be involved in the published “plant-pathogen interaction” pathway, biosynthetic pathway of plant hormones, autophagy and signal transduction before the plant immune system was induced. The function of these candidates will be further defined to understand the resistance mechanism of SA0423 and to develop eQTL and/or SSR markers to apply in marker-assisted selection for improving disease resistance.
Key words:Rice, Bacterial blight disease, Resistance, Mutant, Transcriptomes
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors