All issues
Author:Yaw-Jen Dong and Chien-Chung Chen*
Abstract:
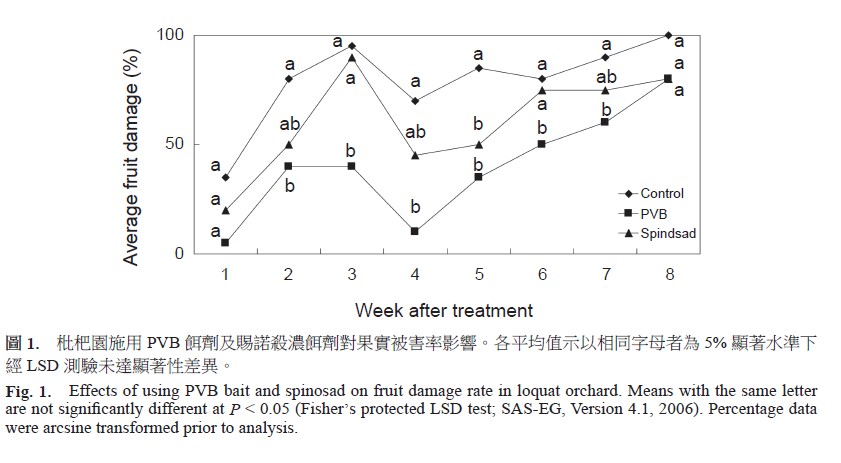
Evaluation of the applicability of oriental fruit fly [Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel)] plant volatile bait (PVB bait) was conducted in 5 m × 5 m × 2 m net-cage and 0.76 ha loquat orchard, respectively. Results of net-cage test showed that 1 d average attracted and killed mortality of fresh new and exposing outdoor for 1, 2, and 3 wk PVB bait to non starvation and gravid female oriental fruit fly were 85.3, 72.0, 60.3, and 62.1%, respectively, and decreased with time. One day average attracted and killed mortality of using 1, 2, 3, and 4 PVB bait were 86.9, 96.0, 94.3, and 92.9%, respectively, and using more than 2 baits did not show higher effectiveness. One-day average attract-and-kill mortality of PVB bait, protein hydrolysate, Spinosad, Torula yeast and yellow sticky paper were 81.3, 74.0, 72.9, 50.3, and 49.5%, respectively. Attract and kill effectiveness of PVB bait is better than those of currently materials used for oriental fruit fly control. Evaluation of PVB bait control effectiveness was conducted in loquat orchard, and the results showed that average fruit damage and number of oviposition puncture number were the lowest in PVB bait treatment plot than in Spinosad and control plots. Although PVB bait has potential to use as oriental fruit fly control substance, further improvement of the persistence and stability of PVB bait is required.
Key words:Bactrocera dorslais, Plant volatile bait, Attractiveness, Fruit fly control
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors