All issues
Author:Tzu-Huan Hung, Jui-Sheng Lai, Su-Yue Lin, Chieh Yang, and Ya-Lin Lee*
Abstract:
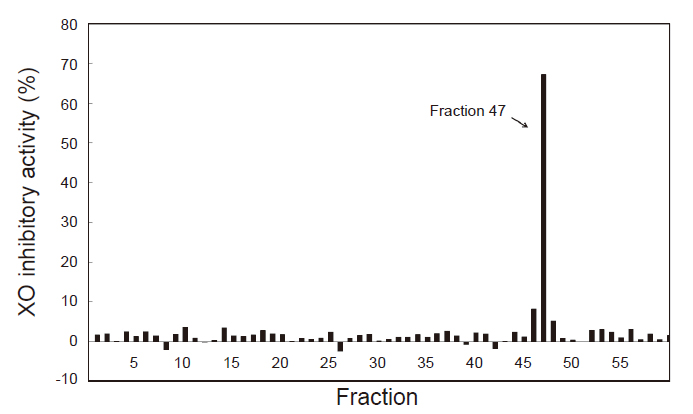
Hyperuricemia is a risk factor for causing gout, diabetes and some metabolic diseases. The reduction of uric-acid biosynthesis and alleviating the symptom of hyperuricemia may be intervened by inhibiting the xanthine oxidase (XO) activity. In this study, the XO inhibitory activity of ethanol or water extracts of 24 indigenous medical plants were evaluated. Results showed that the ethanol extract of Alpinia galanga rhizomes possessed the best XO inhibitory activity. The ethanol extract of Mesona procumbens line ‘Tai E’ showed mild activity as well. The active XO inhibitors in the A. galanga rhizomes were suggested to be (1’S)-1’-acetoxychavicol acetate and p-coumaryl diacetate based on the analytical results of gas chromatography-mass spectrum (GC-MS). Both compounds were reported exhibiting similar XO inhibitory activities as allopurinol, a common medicine for hyperuricemia treatment. These results suggest that A. galanga is a potential herb for developing functional food or therapeutic agent to regulate the biosynthesis of uric acid.
Key words:Hyperuricemia, Xanthine oxidase, Inhibitory activity, Alpinia galangal
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors