All issues
Author:Chin-Chih Chen*, Fen-Lang Chiang, and Chun-Huey Huang
Abstract:
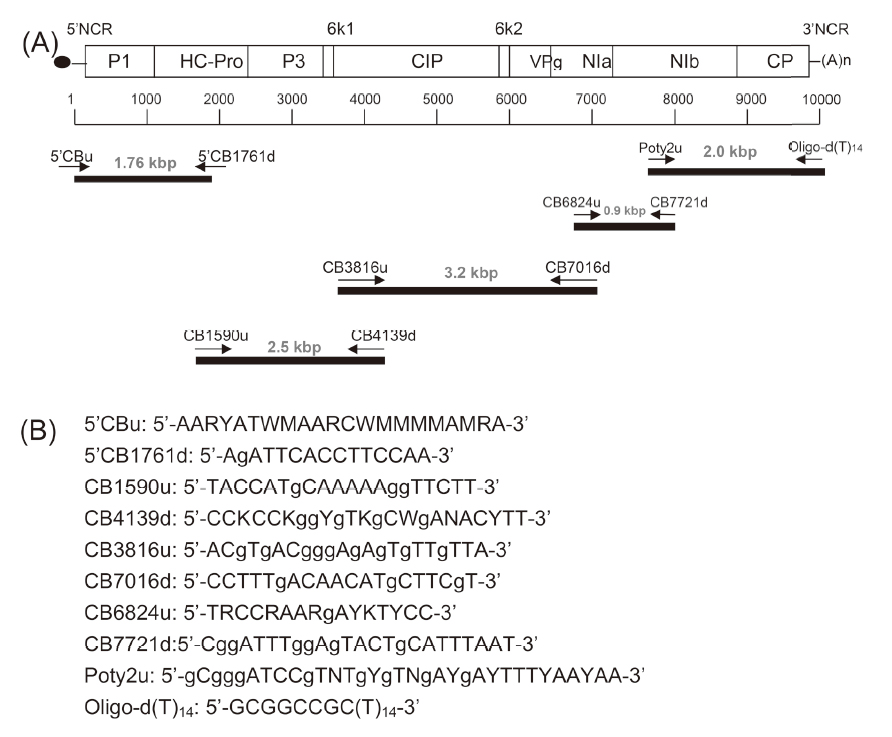
A Potyvirus virus (isolate code CB) was detected from an imported bulb of Christmas bells (Sandersonia aurantiaca Hook), and further identified as the Gloriosa stripe mosaic virus (GSMV) based on the sequences of the coat protein (CP) coding region. The full-length genome sequence of CB was determined, revealing that the CB genome is 9,455 nucleotides (nt) long (accession number EF427894), encoding a polyprotein with 3,052 amino acids (aa). The fragment of 798 nt is coding for 266 aa of the CB CP. Moreover, the CP nt sequences of another five virus isolates, namely CB4 (KT764122) and CB18 (KT764123) from Christmas bells, and GL2 (KT764120), GL3 (KT764124), and GL4 (KT764121) from gloriosa, were also determined and shared 86.5–94.0% aa identities with that of the known GSMV-CP (EU042761) in GenBank, indicating that they are also GSMV isolates. The phylogenetic analysis indicated that the CB, CB4, and CB18 from Christmas bells are closely related. Three primers sets (upstream primers: GSMV7150u, GSMV660u and GSMV500u, and a common downstream primer: GSMVd) were designed from the CB-CP sequence for detection of GSMV. The primer pairs GSMV660u/GSMVd and GSMV500u/GSMVd were useful to amplify the expected amplicons from all of GSMV isolates from Christmas bells and gloriosa in reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The primer pair GSMV715u/GSMVd can amplify the expected 715-bp fragment only from the GSMV isolates of Christmas bells, and is useful for distinguishing those GSMV isolates of Christmas bells from gloriosa’s. The full-length nucleotides of the CB-CP were constructed to the expression vector pET28b, and transformed into Escherichia coli strain Rosetta (DE3) for induction of the overexpressed viral protein. Polyclonal antiserum against the CB-CP, prepared by immunizing the bacterial expressed fusion protein into a rabbit, positively reacted with the GSMV-CP in the virus-infected Christmas bells and gloriosa tissues in indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and western blotting. In this report, GSMV was first found on Christmas bells, and its full-length genome sequence was first completed. The prepared GSMV primer pairs and polyclonal antiserum are helpful to strengthen our ability in GSMV inspection.
Key words:Christmas bells (Sandersonia aurantiaca Hook), Gloriosa stripe mosaic virus (GSMV), Full-length sequence, RT-PCR detection, Polyclonal antibody
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors