All issues
Author:Li-Yu Tsao
Abstract:
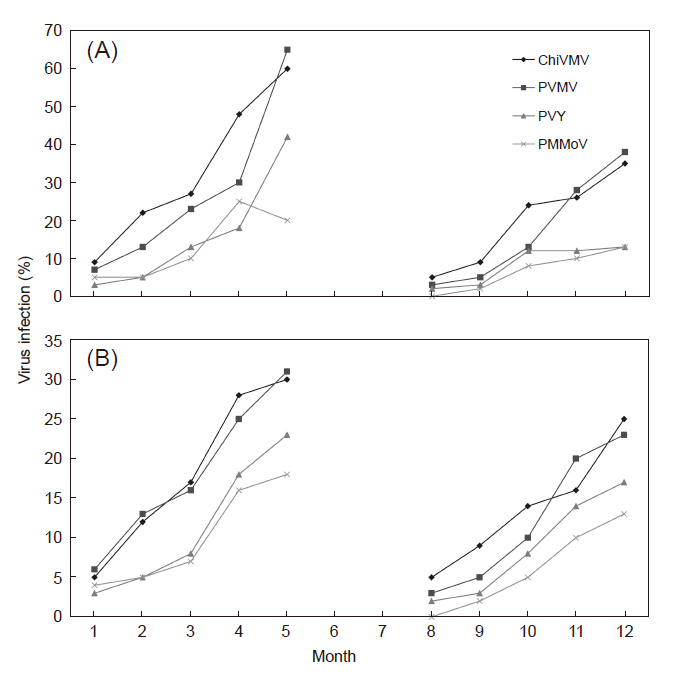
Pepper samples showed virus-like symptoms were collected from Kaohsiung and Pintung areas for virus detection by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (indirect-ELISA) using antisera specific to nine viruses- Capsicum chlorosis virus (CaCV), Chilli veinal mottle virus (ChiVMV), Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV), Pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV), Pepper veinal mottle virus (PVMV), Potato virus Y (PVY), Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), Tomato mosaic virus (ToMV), and Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV). The results showed that ChiVMV was the most prevalent, followed by PVMV. Most samples detected were mix-infected with ChiVMV and PMMoV. Complex infections were likely to cause severe malformation of leaves and fruits, resulting in dwarfing and growth stagnation. In most cases, the symptoms caused by infections of more than two different viruses were more serious than that infected by a single virus. PMMoV could transmit by seed. Seed disinfection was a critical process in preventing virus spread during propagation and production. To directly address the concern, we estimate the efficacy of different disinfectants for treating virus-contaminated seeds. PMMoV can be transmitted through seeds. Direct seed-grinding and grown-out seedlings could be used to measure the PMMoV infection rate of seeds. PMMoV could be detected in 3 of 20 lots of pepper seeds in the grinding sap by ELISA. The PMMoV infection was measured and the virus infection rates were 13%, 18%, and 17%, respectively. The artificially PMMoV- contaminated seeds were placed in a fine mesh bag (100 bags) and soaked in 12.5%, 15%, and 20% trisodium phosphate solution for 10 min, 20 min, and 30 min, respectively, and then rinsed with running water for about 60 min. 1% sodium hypochlorite was used to remove the bacteria on the surface of the seed and put it on wet filter paper to make it germinate. The virus infection rates of the seedlings were investigated, in which the solution was treated with 12.5% trisodium phosphate solution for 30 min (the virus infection rate was 5%). Treatment with 15% trisodium phosphate solution for 30 min (virus infection rate 3%) and 20% trisodium phosphate solution for 20 min (virus infection rate 5%) had the best ability to remove PMMoV. In terms of equipment disinfection tests, the detoxification effect of 5% sodium hypochlorite and 0.5% sodium hypochlorite in three tests can reach 95% or more, followed by 20% skim milk powder.
Key words:Pepper mild mottle virus, Disinfection of cutting tools, Seed disinfection
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors