All issues
Author:Wei-Ting Lee, Ya-Lin Lee, Yu-Tang Tung, Chun-Ching Wu, and Gow-Chin Yen*
Abstract:
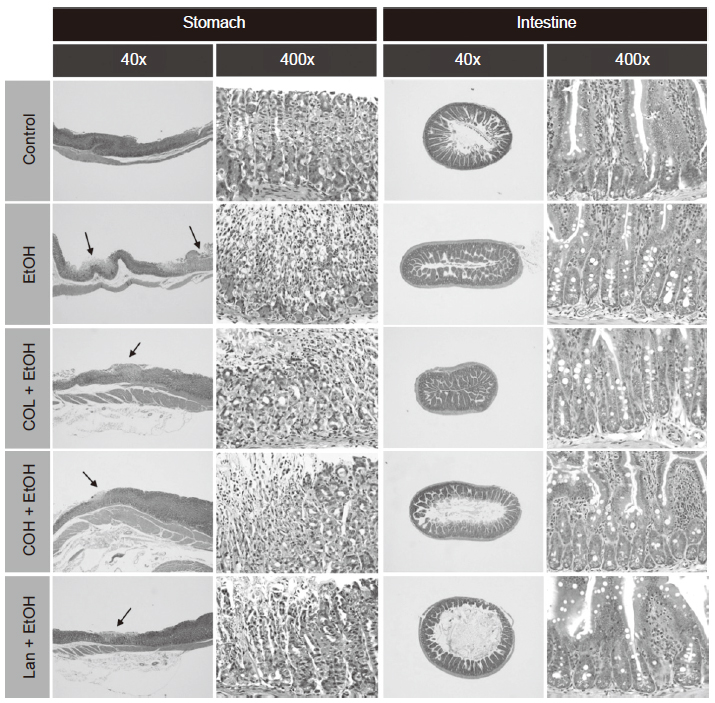
The gastrointestinal disorders such as peptic ulcer become a common problem nowadays, which is due to the dietary habit changes, stressed lives and alcoholism. Camellia oil is commonly used in Taiwan and has been shown with healthy effects for gastrointestinal tract in folk medicine. Our previous study has been demonstrated that camellia oil could prevent the gastric mucosal damage caused by ethanol. This study was aimed to further confirm whether the effects of different sources or processes of camellia oils have the same effect. In this study, the rat normal gastric surface mucous cell line (RGM-1) cells and BALB/c mice were used in ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage model. The results indicated that the ethanol-induced RGM-1 cell mortalities were significantly increased in those pretreated with camellia oils, and the oil with the highest bioactivity was chosen for further animal experiment. Animal experiments showed that ethanol (5 mL kg-1 B.W.) induction for an hour can cause gastric mucosal injury. However, pretreatment of mice with camellia oil (1 mL kg-1 B.W. and 2 mL kg-1 B.W.) for 3 wk or lansoprazole (30 mg kg-1 B.W.) for 1 wk effectively improved ethanol-induced gastric injury, enhanced mucosal mucus secretion, antioxidant enzyme activities including catalase, glutathione S-transferase (GST), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and glutathione reductase (GRd), and alleviated inflammatory cytokines by suppressing the production of COX-2 and IL-1β induced by ethanol in gastric tissue. In conclusion, the camellia oil could alleviate the ethanol-induced gastric injury by reducing oxidative damage and inflammation. The results of this study can be applied to develop the gastrointestinal-related functional products in the future, and thereby enhance the values of indigenous agricultural products.
Key words:Camellia oil, Peptic ulcer, Ethanol, Inflammatory cytokines
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors