All issues
Author:Yuan-Kai Tu, Yu-Wei Feng, Lit-Fu Chan, Shu Chen, Yen-Chun Lin, and Han-Wei Chen*
Abstract:
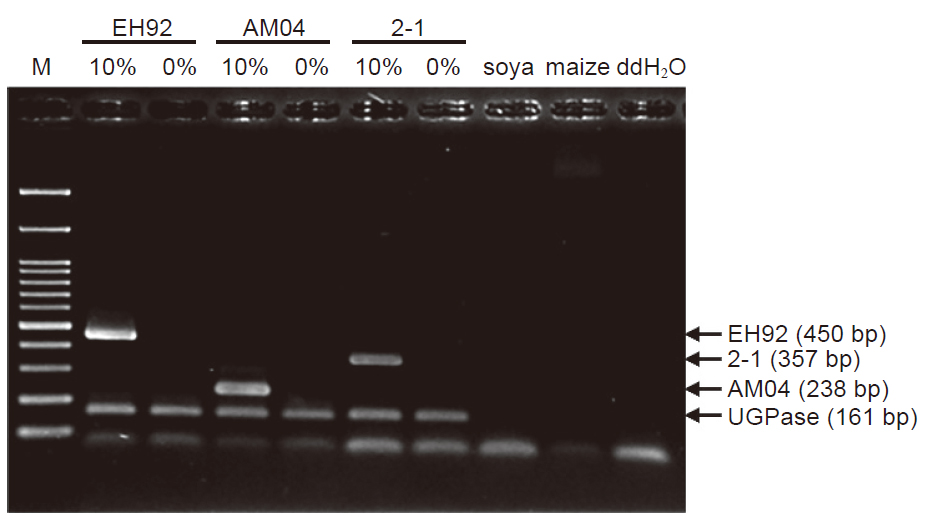
Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) is known as one of the most important food crops in the world and has high application in industry and feed. In this study, we present a multiplex polymerase chain reaction (mPCR) method for simultaneous detection of genetically modified (GM) potatoes. Quadruplex PCR assay targeting three event-specific sequences and the taxon-specific endogenous reference gene (UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase; UGPase) were established. All potato DNA samples generated the expected PCR products, and the detection method performed robustly and specifically with various combinations of mixed GM potato events. The limit of detection (LOD) of each single GM sample in our mPCR detection assay was 0.5%. Furthermore, a proficiency test returned from four research sectors also indicated that our detection method had good reproducibility and repeatability. We also developed a simple, rapid and cost-efficient nucleic acid extraction method coupled with multiplex PCR and followed capillary electrophoresis. These results suggest that our methods are suitable for detecting multiplex PCR targets and have the potential for screening unknown genetically modified potato samples through a simple procedure.
Key words:Potato, mPCR, Detecting method
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors