All issues
Author:Chien-Hui Syu, Chia-Yi Cheng, Tsang-Sen Liu, Dong-Hong Wu, Horng-Yuh Guo, and Yu-Wen Lin*
Abstract:
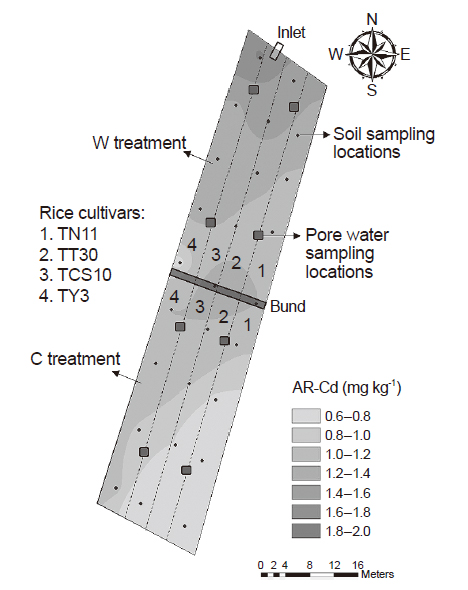
Rice is a major staple crop in Asia area. The studies aimed at reducing cadmium (Cd) accumulation in rice grain have received much concern in recent years. Water management is a well-known agronomic practice for reducing Cd accumulation in rice grain, which is not only environment-friendly feasible but also easy to operate by farmers. However, there were few studies comparing the differences in Cd accumulation in rice plants among various rice cultivars under different water managements. Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate the effect of water management on the Cd availability in soils, Cd accumulation in rice plants and grain yield of different rice cultivars. Two water management methods (conventional and flooded) and four rice cultivars (‘TN11’, ‘TT30’, ‘TCS10’ and ‘TY3’) were used in this study, and the soil redox potential, Cd concentration in pore water, grain yield and Cd concentration in rice plants were determined during the experimental period. The results of this study indicating the flooded treatment can effectively reduce the Cd concentration in pore water, and further decrease the Cd accumulation in the root (59.1–90.7%), shoot (48.9–93.9%) and brown rice (43.0–93.9%), compared with conventional practice. Based on the results of translocation factors, it indicates that the mechanism of flooded treatment to reduce Cd accumulation in brown rice is the decrease of Cd availability in soils, rather than reduce the translocation capability of Cd in plants. The results of this study confirm that flooded treatment can effectively reduce Cd accumulation in brown rice of japonica and indica cultivars. Therefore, it suggests that the Cd accumulation in rice grain will be reduced markedly through increasing the flooded time in Cd-containing paddy field.
Key words:Cadmium, Paddy rice, Water management, Field experiment, Rice cultivar
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors