All issues
Author:Chin-Chih Chen*, Fen-Lang Chiang, Ying-Huey Cheng, and Jia-Yi Liao
Abstract:
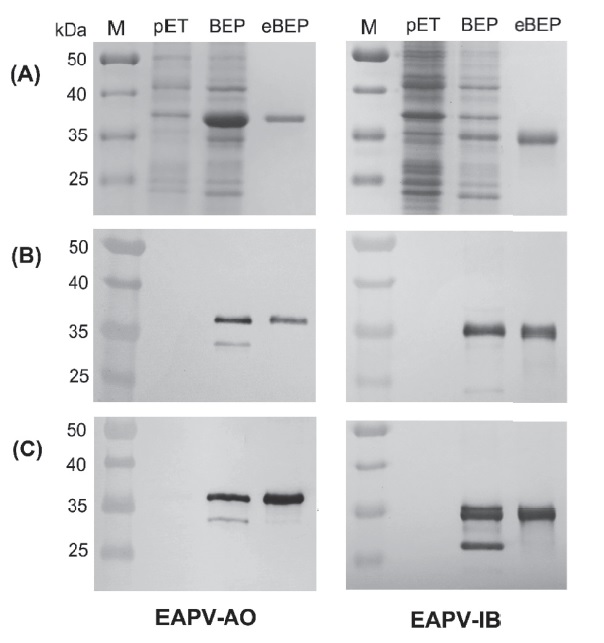
When the virus-infected passion fruits showed woodiness symptoms on fruits, the fruits were deformed and smaller resulting in a low juice rate, poor flavor and quality, which could cause a great impact on yield. Two East Asian Passiflora viruses (EAPV-AO and EAPV-IB) and Telosma mosaic virus (TeMV) are the three main potyviruses infecting passion fruits in Taiwan. In this study, the polyclonal antibodies against the coat proteins (CP) of EAPV-AO and EAPV-IB were respectively prepared from immunizing rabbits with the bacterial expressed viral CPs, revealing that both antibodies have a wide-spectrum response with 19 tested potyviruses. In indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (indirect ELISA), the equivalent mixture of polyclonal antibodies against the CPs of EAPV-AO and EAPV-IB, denoted Anti-EAPVmix, could also be used to detect passionfruit isolates of TeMV from Taiwan and Thailand, and to improve the detection rate of EAPV-AO, EAPV-IB, and TeMV. The distribution of viruses on plant branches was detected by Anti-EAPVmix. The virus was detected at a high rate from the upper part near new leaves, which is recommended for sampling. Our result showed that the mixture of EAPV polyclonal antibodies can be used to detect not only the three major passiflora viruses in Taiwan but also other potyviruses to save the detection time and costs. The detection method can strengthen the field survey of passiflora viruses and the internal control of healthy seedlings.
Key words:Passiflora potyviruses, Polyclonal antibody, Antibody mixture, Wide-spectrum detection
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors