All issues
Author:Yi-Chung Chiu*, Feng-Chyi Lin, Hsien-Tzung Shih, and Chin-Ling Wang
Abstract:
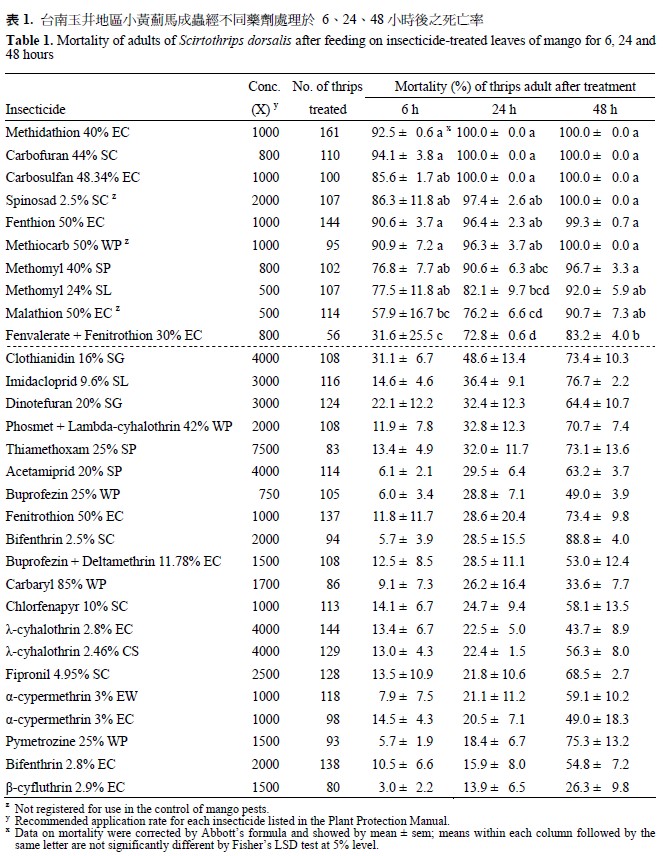
Scirtothrips dorsalis Hood is a serious pest of mango (Mangifera indica Linn.) in Taiwan. This study was conducted to determine efficacy of 30 insecticides for control of adult S. dorsalis by the feeding trials on insecticide-treated leaves of mango. Results showed that, after feeding for 24 hours, the mortality of thrips was the highest (90.6 to 100%) for the treatments of methidathion 40% EC, carbofuran 44% SC, carbosulfan 48.34% EC, spinosad 2.5% SC, fenthion 50% EC, methiocarb 50% WP, and methomyl 40% SP. The mortality of thrips was moderate (72.8 to 82.1%) for the treatments of methomyl 24% SL, malathion 50% EC, and fenvalerate mixed with fenitrothion 30% EC, whereas the mortality was low (< 50%) for the rest of the 20 insecticides tested. This study suggests that the seven insecticides (methidathion, carbofuran, carbosulfan, spinosad, fenthion, methiocarb, and methomyl) may be of potential for control of S. dorsalis in commercial fields of mango in Taiwan.
Key words:Thrips, Scirtothrips dorsalis, Mango, Mangifera indica, Insecticides, Toxicity
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors