All issues
Author:Chan-Lee Ho, Guang-Jauh Shieh, Wen-Long Tsaur and Hung-Shung Lu*
Abstract:
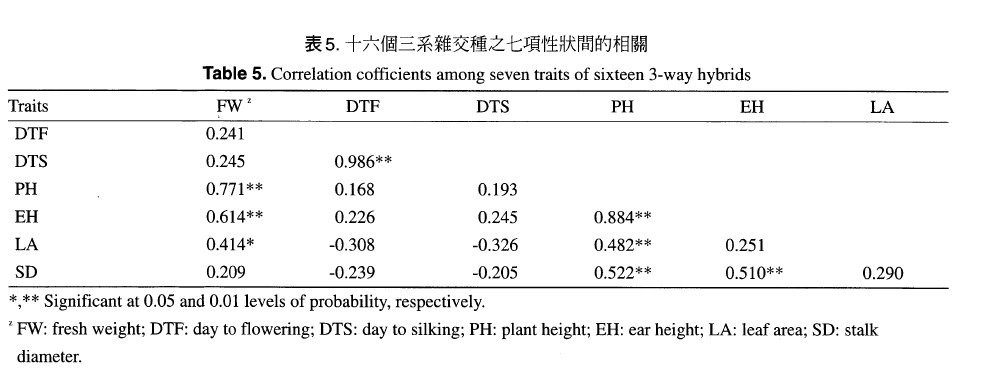
Four inbred lines, namely, Hi28 (A), TA85-58 (B), Tx601 (C) and TA82-36 (D), and four single cross hybrids, namely, TNG1 (E×F), TNG2 (G×F), TNG3 (I×J) and TNG351 (K F×L), and their sixteen three-way cross hybrids of forage maize were evaluated for agronomic traits and forage yield in the spring crop of 1998. Results of analysis of variance showed that days to flowering, days to silking, plant height, ear height, leaf area, stalk diameter and forage fresh weight were significantly correlated among these twenty-four genotypes. The forage fresh weight was positively correlated to plant height, ear height and leaf area, but it was not correlated to days to flowering, days to silking and stalk diameter in three-way cross hybrids. The relationships may be used as selection indicators in three-way cross hybrid breeding program. No significant differences were found between forage fresh weight produced from single cross hybrids and three-way cross hybrids. Among three-way cross hybrids, (E×F) ×D (57,563 kg ha-1), (G×F) ×D (53,625 kg ha-1) and (I×J) ×D (50,375 kg ha-1) were the better combinations in terms of forage fresh weight. These three hybrids were all crossed with the inbred line D, and expressed a higher hybrid potence value and an over dominance character. Results suggest that a higher forage production hybrid can be made from three-way cross breeding by selecting parental lines with high-yield potential.
Key words:Forage maize, Single cross hybrid, Three-way cross hybrid, Potence value
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors