All issues
Author:Yi-Chen Lin, Chun-Tang Lu, Meng-Li Wei, and Hsiu-Ying Lu*
Abstract:
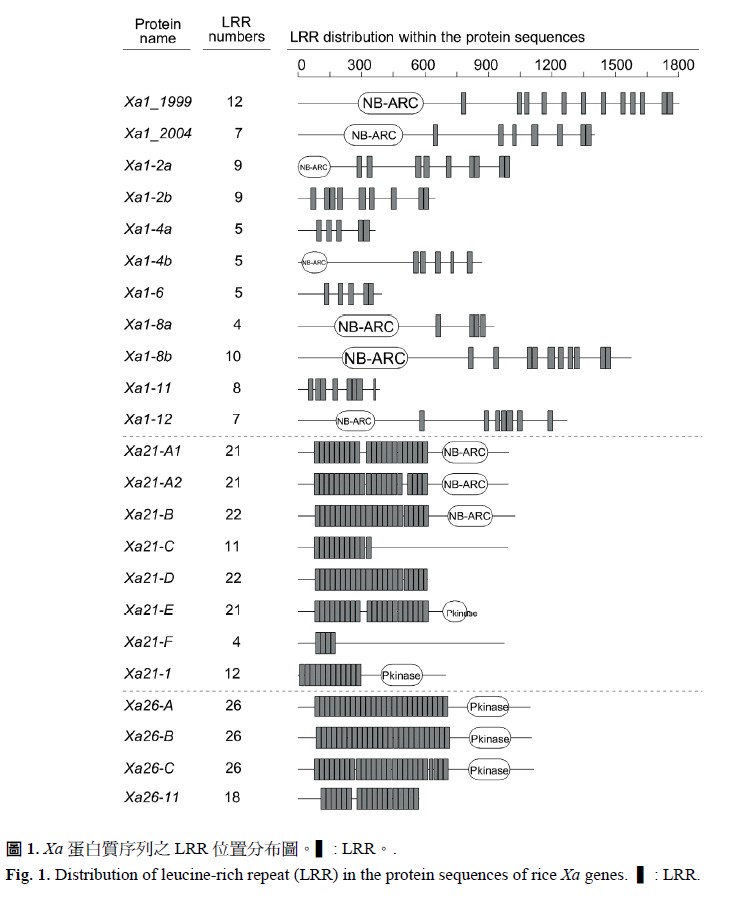
Since leucine-rich repeat (LRR) is known as a domain of protein specific to disease resistance genes, it is used to study the genes of rice with resistance to bacterial blight caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. The CDS (coding domain sequence) and full-length cDNA sequences of the completely sequenced genes were obtained through the access from public databases of NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) and KOME (Knowledge-based Oryza Molecular Biological Encyclopedia) and they were used to identify each LRR fragment in translated protein sequences through Pfam protein families database. Results showed that only Xa1, Xa21 and Xa26 genes were found to possess LRRs in their protein sequences. When bioinformatics and statistical methods were used for further comparative analysis of distribution and amino acid composition for these LRRs among Xa protein sequences, LRRs of Xa1 were loosely located after NB-ARC (nucleotide-binding adaptor shared by APAF-1, R proteins, and CED-4) in the protein sequences, whereas LRRs of Xa21 and Xa26 were densely located before NB-ARC or P-kinase (protein-kinase). It appeared that the first one or two LRRs of the gene Xa1 proteins in proximity to NB-ARC were distant from the other LRRs, but no similar phenomenon was observed within the protein sequences of the Xa21 and Xa26 genes. The LRRs of these three Xa genes mainly consisted of hydrophilic amino acids, with the highest frequency for leucine, followed by neutral serine. The LRRs of Xa1 protein sequences had different frequencies for some amino acids compared to LRRs of Xa21 and Xa26. These findings are useful in understanding of the structural variation of LRRs in protein sequences among Xa genes with resistance to bacterial blight of rice.
Key words:Rice, Xa genes, Bacterial blight, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, Leucine-rich repeat, Amino acids
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors