All issues
Author:Jen-Ren Chen, Hsin-Mei Ku, Jau-Yeuh Wang, and Min-Tze Wu*
Abstract:
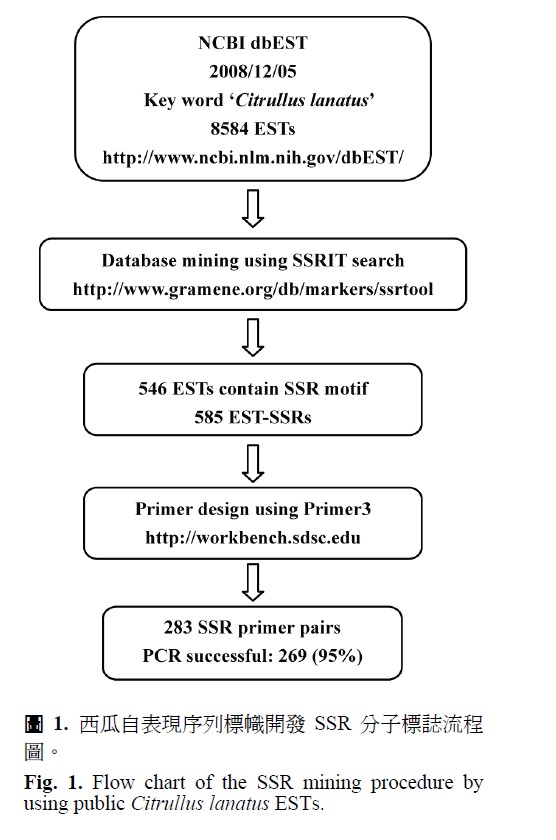
Microsatellite or simple sequence repeats (SSRs) are molecular markers of choice for many genetic studies. The exploiation of SSR markers from cDNA and expressed sequence tag (EST) has been described for many plant species. These markers are important for genome mapping as well as variety identification. In this study, 546 SSR-containing sequences were identified from 8,584 Citrullus lanatus ESTs, retrieved from the NCBI dbEST database. A total of 585 EST-derived SSRs, with tri-nucleotide motifs most abundant among them, were obtained. Primer sequences flanking SSR motifs were successfully designed from 283 C. lanatus ESTs. Primers were tested for their ability to amplify SSR loci and polymorphism evaluated among commercial F1 cultivars. Approximately, 95% designed SSR primers were successfully used to amplify PCR products and 24 out of 269 SSR markers revealed polymorphisms among twenty-two watermelon cultivars. These EST-derived SSR markers could be a valuable resource for expanding C. lanatus SSR markers and may contribute to establishment of C. lanatus SSR genetic linkage map.
Key words:Citrullus lanatus, Watermelon, Microsatellite, Simple sequence repeat, Expressed sequence tag, Molecular marker
Download:![]() PDF Links
PDF Links
- 1. Development of Tractor-Mounted Seedling Transplanter for Sweet Potato
- 2. Synergistic Effect of Additional Gas on the Toxicity of Phosphine to Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae)
- 3. Effects of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Growth Traits and Plant Elements in Purple Leafy Sweet Potato
 Submit your manuscript
Submit your manuscript
 Guide for authors
Guide for authors